GUM TREATMENT
Gum Treatment
Gum treatment refers to a variety of dental procedures aimed at preventing, managing, and treating gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis) as well as improving overall gum health. It can involve non-surgical treatments, like scaling and root planing, as well as surgical treatments in more severe cases.
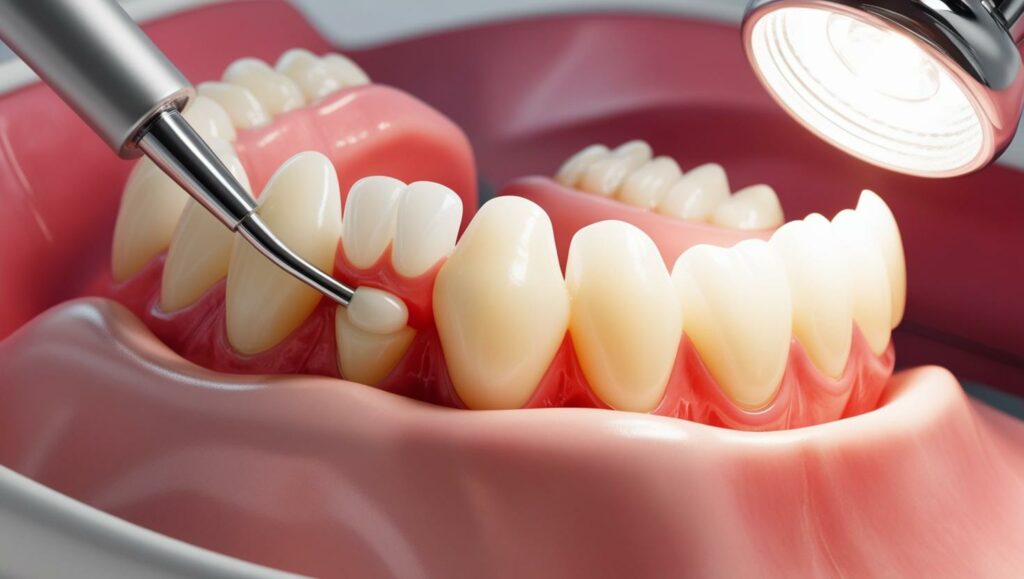
Why is Gum Treatment Needed?
Gum treatment is necessary to:
Prevent Gum Disease: Gum disease (gingivitis and periodontitis) is caused by plaque and tartar buildup. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss, bad breath, and other health complications.
Prevent Tooth Loss: Severe gum disease can lead to the destruction of the tissue and bone supporting your teeth, which can result in tooth mobility or loss.
Improve Overall Health: Gum disease has been linked to other health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues, so maintaining healthy gums is vital.
Reduce Inflammation and Pain: Treatment helps reduce gum swelling, bleeding, and discomfort, improving your quality of life.
Procedure for Gum Treatment
The procedure for gum treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
Non-Surgical Treatments:
Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
Antibiotics: Used to control infection and bacteria, often in the form of gels or oral medication.
Surgical Treatments (for severe cases):
Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): The gums are lifted back, and tartar is removed. The gum is then sutured back in place for a tighter fit around the tooth.
Bone Grafting: Used to regenerate bone lost due to severe gum disease.
Soft Tissue Grafts: To repair or restore gum tissue lost due to gum recession.
Post-Treatment Care
After gum treatment, it’s important to follow your dentist’s instructions to ensure proper healing and long-term gum health:
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss gently but effectively to prevent future plaque buildup.
Avoid Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco can slow healing and worsen gum disease.
Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash: This can help control bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Dietary Changes: Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support gum health, like Vitamin C.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Follow-up appointments will help monitor healing and prevent recurrence of gum issues.
Pain Management: Your dentist might recommend pain relief or antibiotics to help manage discomfort and prevent infections.
Benefits of Gum Treatment
Prevents Further Gum Damage: Early intervention prevents more severe complications like tooth loss or bone deterioration.
Improves Gum Health: Treatment helps your gums become healthier, reducing inflammation, bleeding, and tenderness.
Reduces Bad Breath: Treating gum disease can eliminate persistent bad breath caused by bacteria and infection.
Restores the Function of the Teeth: Healthy gums help to stabilize the teeth and prevent them from becoming loose.
Improves Overall Health: Reducing gum inflammation can have a positive impact on overall systemic health, lowering the risk of other chronic diseases.
Regular gum care and visits to the dentist can significantly enhance the effectiveness of any treatment and prevent the recurrence of gum issues.